Theoretical - Heat Transfer
Heat transfer is a discipline of thermal engineering that concerns the generation, use, conversion, and exchange of thermal energy (heat) between physical systems.
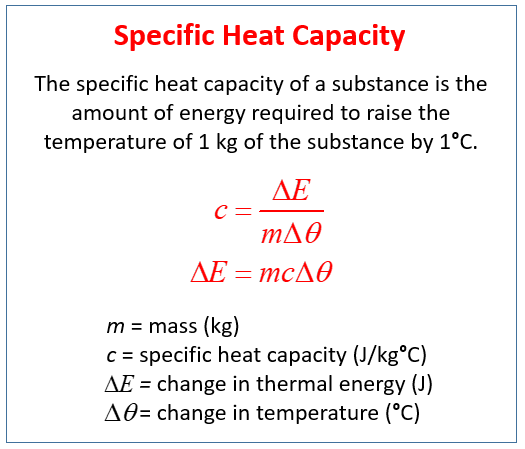
Ideally, given heat from one matter is equal to received heat from other. Using this approach and with the help of Specific Heat Capacity Formula we can calculate the final (equilibrium) temperature when two different matter touch each other.
One way to find the final temperature value we can use below formula.
| Final Temperature | = |
|
But this classical approach is so easy to write.
Instead, we will use symbolic programming using Python’s SymPy package.
Symbolic programming is a programming paradigm in which the program can manipulate its own formulas and program components as if they were plain data.
SymPy are capable of computing symbolic expressions with variables. Using symbolic programming we can we can solve problems like this. You can learn more about sympy from this tutorials.
Practical - Heat Transfer
- Classical Approach
class Matter(object):
def __init__(self, mass, constant, temperature):
self.mass = mass
self.c = constant
self.temp = temperature
def heatTransfer(m1, m2): # Find equilibrium temperature
# equilibrium = (m1*c1*t1 + m2*c2*t2) / (m1*c1 + m2*c2)
equilibrium = (m1.mass * m1.c * m1.temp + m2.mass * m2.c * m2.temp) / (m1.mass * m1.c + m2.mass * m2.c)
return equilibrium
hot_water = Matter(6, 1, 85) # Matter 1
cold_water = Matter(8, 1, 10) # Matter 2
t_balance = heatTransfer(hot_water, cold_water)
print(t_balance)
- Symbolic Programing Approach
class Matter(object):
def __init__(self, mass, constant, temperature):
self.mass = mass
self.c = constant
self.temp = temperature
m1 = Matter(6, 1, 85) # Matter 1
m2 = Matter(8, 1, 10) # Matter 2
# Import sympy
from sympy import *
# Define symbols
T = symbols('T') # T = equilibrium
# Q1 - Q2 = 0
q1 = m1.mass * m1.c * (T - m1.temp)
q2 = m2.mass * m2.c * (m2.temp - T)
e = solve(q1 - q2, T) # Returns a list of rational number solutions
print(e[0].evalf()) # Print float value of first (and only) solution